Rotator discs are a great tool to improve dancers’ pirouette form and are also useful for non-dancers to experience postural alignment along a center axis. Although proper alignment prevents injuries and allows our bodies to move most efficiently, it can be challenging to maintain this interlocking jigsaw-like relationship when put in motion. A spinning motion along a central axis using rotator discs can proprioceptively illustrate an understanding of alignment better than words ever could. Your client will either maintain balance and have a conscious experience of a “center” line through the body like that of the lead of a pencil, or she will lose balance and have a warping disjointed experience demonstrating that posture was not maintained.
Rotator discs come in different sizes and are basically two circular plates with ball bearings in the center. You will want to choose a size that is large enough for your client to stand on with both feet side by side—12” is generally good choice. In preparation for this exercise, be sure your client has a clear understanding of proper alignment in a static position and how to engage her core muscles. (See article “The Use of Imagery to Help Your Client Find Lift Through the Core.”) Do not put any person into this exercise who has difficulty balancing on one leg, as the exercise would be too advanced. Make sure to spot your client in case she loses her balance, and allow plenty of floor space around the disc free from any obstacles.
Start your client with one foot on the floor and the other foot placed on the disc. An outside or en dehors turn has the right foot on the disc and requires a counterclockwise turn with the left foot pushing off the floor and then stepping onto the disc. For an inside or en dedans turn to the right, the right foot starts on the disc with the left foot pushing off the floor and turns clockwise. Use the back foot to push off the floor providing momentum for the turn and step quickly onto the disc with both feet.
Applying too much force will throw your client off-balance or increase the revolutions to possibly make your client dizzy. It is best to start with minimal force until your client gets used to how much pressure to apply against the floor. Have your client continue to turn until the disc slows and comes to a stop. Be sure to practice both sides and change directions every few turns. If your client is a dancer, have her practice “spotting” in the turn.
 The placement of the arms should be considered in the turn. You can have your client hold her arms by her sides or in front of her as if she is holding a ball. If you have a ball that is the size of a beach ball it can be useful to actually hold the ball at the chest. Note that your client might feel more secure having her arms free when first attempting this exercise in case she loses her balance.
The placement of the arms should be considered in the turn. You can have your client hold her arms by her sides or in front of her as if she is holding a ball. If you have a ball that is the size of a beach ball it can be useful to actually hold the ball at the chest. Note that your client might feel more secure having her arms free when first attempting this exercise in case she loses her balance.
If your client is a dancer, the arm placement can be more complicated with the preparatory position in ballet 3rd position moving to 1st position in the turn. Dancers can sometimes lose the volume of 1st position when turning, so holding the ball can give your client a sense of width between the elbows. Make sure that your client anchors her scapulae as well so that the arms are connected to the back with strength.
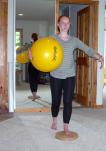
inside or en dedans turn to the left
The ball should be placed in the “following” arm, not the lead arm. The arm that follows into the turn is more significant since it provides the “snapping in” effect providing momentum. If this arm is not lively and connected into the back the turn will lose energy and stability. Practicing this movement first with the ball patterns the arm to move toward the midline of the body with volume and proper timing.
Rather than just standing on the rotator disc with both feet flat, dancers can progress to having the working leg in forced arch, coupé and then passé. As the level of difficulty increases, be careful to decrease the torque exerted against the floor or the turn will be difficult to maintain. Parallel and turned out positions are both suitable for practice, but parallel may be preferable for the general public or contemporary dancers.
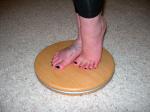
forced arch foot placement
Rotator discs can effectively teach the concept of center. Your client must stabilize her core (the center of gravity) in addition to holding postural alignment (center axis). When using a rotator disc, the central axis of the body is like the pole in tetherball and the turning action represents the ball going around the pole. It is essential to have the body aligned or the turn will wobble like a tetherball would around a bent pole. Your client receives immediate feedback as to her success and can adjust accordingly. The experience of turning on the rotator disc becomes her instructor and teaches the concept of center better than your explanation ever could.
